Childhood Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors
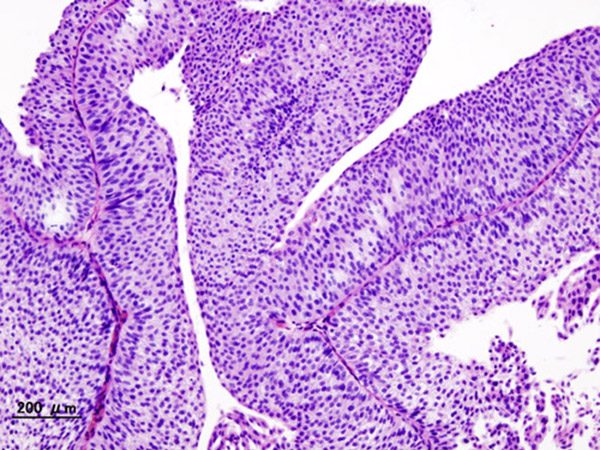
Central nervous system (CNS) embryonal tumors form in embryonic cells that remain in the brain after birth. This type of tumor tends to spread through the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to other parts of the brain and spinal cord. While CNS embryonal tumors may be malignant or benign, in children most are malignant.
Malignant brain tumors are likely to grow quickly and spread into other parts of the brain. Although cancer is rare in children, brain tumors are the third most common type of childhood cancer, after leukemia and lymphoma.
There are different types of CNS embryonal tumors, including medulloblastomas and four types of CNS primitive neuroectodermal tumors – CNS neuroblastomas, CNS ganglioneuroblastomas, medulloepitheliomas, and ependymoblastomas.
Childhood Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)Source: National Cancer Institute