Editors’ Picks, August 2025: Liquid Biopsy for Brain Cancer, Therapeutic Strategies for Prostate Cancer, and More
This month, the editors of the 10 peer-reviewed journals published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) have highlighted a DNA fragmentome-based liquid biopsy approach for the detection of brain cancer, new strategies for treating prostate and colorectal cancers, and factors that influence immunotherapy efficacy, among other topics.
Keep reading for the abstract of each highlighted study, and follow the links for the full-text articles, which are freely available for a limited time.
Journal: Blood Cancer Discovery
Clinical Significance of TP53-Mutant Clonal Hematopoiesis Across Diseases
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) has broad clinical relevance, and TP53 plays various roles within cells. However, the gene-specific and cross-disease significance of CHIP with TP53 mutations (TP53-CHIP) remains unclear. In this study, we evaluated TP53-CHIP using targeted sequencing data of 140,597 individuals without hematologic neoplasms in BioBank Japan. We identified 1,157 individuals with TP53-CHIP and clarified the characteristics of mutations and carriers. TP53-CHIP was associated with poor overall survival, especially because of lymphoid neoplasms and respiratory disease, in addition to myeloid neoplasms. Significant interactions accompanied by excess risks were observed between TP53-CHIP and lifestyle factors for disease-specific mortality: acetaldehyde exposure (resulting from the interaction between drinking and the germline variant of ALDH2) for myeloid neoplasms and smoking for respiratory disease. The clinical significance of TP53-CHIP was sometimes largely independent of variant allele fractions. These findings elucidate aspects of disease pathogenesis and inform personalized risk management.
Significance: TP53-CHIP contributed to a wide range of outcomes besides myeloid neoplasm mortality. TP53-CHIP, when combined with environmental factors, showed a remarkably higher risk for disease-specific mortality, accompanied by excess risks.
Journal: Cancer Discovery
Detection of Brain Cancer Using Genome-wide Cell-free DNA Fragmentomes
Diagnostic delays in patients with brain cancer are common and can impact patient outcome. Development of a blood-based assay for detection of brain cancers could accelerate brain cancer diagnosis. In this study, we analyzed genome-wide cell-free (cfDNA) fragmentomes, including fragmentation profiles and repeat landscapes, from the plasma of individuals with (n = 148) or without (n = 357) brain cancer. Machine learning analyses of cfDNA fragmentome features detected brain cancer across all-grade gliomas (AUC = 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.87–0.93), and these results were validated in an independent prospectively collected cohort. cfDNA fragmentome changes in patients with gliomas represented a combination of fragmentation profiles from glioma cells and altered white blood cell populations in the circulation. These analyses reveal the properties of cfDNA in patients with brain cancer and open new avenues for noninvasive detection of these individuals.
Significance: Brain cancer is one of the deadliest and most challenging cancers to detect with liquid biopsy approaches in blood, hampering efforts for earlier noninvasive diagnosis. We have developed a machine learning genome-wide cfDNA fragmentation method that provides a sensitive and accessible approach for brain cancer detection.
This article was featured on the cover of the August issue. Learn more about cfDNA fragmentome-based liquid biopsy in a recent story on the AACR blog.

Journal: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention
Background: Accurate reporting of state-specific endometrial cancer incidence is important for informing cancer control efforts and may lead to new hypotheses about environmental and/or geographic risk factors. Previous studies have demonstrated the importance of accounting for hysterectomy prevalence when estimating state-level endometrial cancer incidence rates as hysterectomy prevalence varies by geographic region.
Methods: We used the Cancer in North America Public Use Dataset produced by the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries to identify incident endometrial cancer cases among women ≥20 years of age diagnosed from 2010 to 2019. We estimated state-specific hysterectomy-corrected, age-adjusted incidence rates overall and by histology. State-specific hysterectomy prevalence data were obtained from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
Results: Hysterectomy prevalence was highest in Southern and Midwestern states and lowest in the Northeast. Although uncorrected endometrial cancer incidence rates were highest in the Northeast, hysterectomy-corrected rates were highest in states within the Midwest and Appalachia. Geographic patterns of the hysterectomy-corrected incidence of endometrioid cancer resembled those of endometrial cancer overall. In contrast, corrected rates of non-endometrioid cancer were highest in the South and in certain states within the Northeast and Midwest. There was no overlap in the top 10 states with the highest rates of endometrioid and non-endometrioid cancers, respectively.
Conclusions: State-specific, hysterectomy-corrected incidence rates of endometrial cancer vary by histology, suggesting potential differences in behavioral, sociodemographic, and/or environmental exposures at the state level.
Impact: This study presents an accurate assessment of US endometrial cancer rates and emphasizes the importance of hysterectomy correction for geographic comparisons.
Journal: Cancer Immunology Research
The efficacy of most immunotherapies for prostate cancer is limited by poor tumor immunogenicity as evidenced by minimal T-cell infiltration. Treatment with T cells engineered to express T-cell receptors (TCR) targeting prostate-specific antigens offers a potential solution by bypassing endogenous T-cell repertoire limitations. Through differential gene expression analysis, we have identified kallikrein-related peptidases 2, 3, and 4 (KLK2, KLK3, and KLK4) and homeobox B13 (HOXB13) as strictly prostate lineage–specific genes with high expression in prostate cancer and no expression in healthy tissues of risk. Naturally processed peptides derived from these antigens were identified, enabling T-cell enrichment using peptide–MHC multimers. High-avidity T cells targeting these antigens were isolated from allogeneic HLA-mismatched donors. After screening for on-target tumor specificity and absence of off-target reactivity, TCRs recognizing KLK4 in HLA-A*02:01 and KLK3 in HLA-B*35:01 were sequenced and further tested. TCRs were expressed in T cells through TCR gene transfer and TCRs with best performance were selected. Using combinatorial peptide library scanning, the cross-reactive potential of the KLK4-A2 and KLK3-B35 TCRs was analyzed. The KLK3-B35 TCR exhibited cross-reactivity against two additional peptides derived from LOXHD1 and CDH23, with broad tissue expression, and was therefore excluded. The KLK4-A2 TCR was highly specific for the KLK4 peptide. Further testing confirmed effective cytotoxic killing potential of KLK4-A2 TCR in vitro and in vivo, underscoring its therapeutic potential. These findings highlight the promise of the KLK4-A2 TCR for prostate cancer immunotherapy and demonstrate that prostate-specific antigens can be effectively targeted using TCR gene transfer strategies.
This article was featured on the cover of the August 2025 issue.
Journal: Cancer Prevention Research
Advanced age and obesity are major risk factors for breast cancer progression, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In this study, we interrogated (i) whether these factors interact to promote TNBC progression and (ii) whether weight loss mitigates the separate and combined effects of aging and obesity on TNBC. We demonstrate that aging and diet-induced obesity interact to promote TNBC growth in mice. Transcriptomic analysis revealed the suppression of antitumor immunity in tumors from aged and/or obese mice. Weight loss via intermittent calorie restriction reduced tumor growth and restored immune-related gene signatures to reverse the protumor effects of aging and/or obesity. Using publicly available genomic datasets from murine studies of obesity, weight loss, and TNBC, we identified a consensus transcriptomic signature of obesity-driven immunosuppression that predicted the survival of patients with breast cancer. This consensus signature was also suppressed by aging, obesity, and their combination. Intermittent calorie restriction reversed the effects of aging and/or obesity on the consensus signature. We conclude that aging and obesity interact to limit antitumor immunity and enhance TNBC progression and that these adverse effects can be disrupted by weight loss.
Prevention Relevance: Advanced age and obesity are important risk factors for the development and progression of breast cancers, including TNBC. We demonstrate that the suppression of signatures of antitumor immunity is a common feature of accelerated tumor progression in TNBC. We show that weight loss achieved through calorie restriction can restore such markers.
A related commentary was published in the August 2025 issue.
Journal: Cancer Research (August 1 issue)
Ferroptosis is a nonapoptotic form of cell death driven by iron-dependent lipid peroxide accumulation. Colorectal cancer cells feature elevated intracellular iron and reactive oxygen species that heighten ferroptosis sensitivity. The ferroptosis inducer (S)-RSL3 [(1S,3R)-RSL3] is widely described as a selective inhibitor of the selenocysteine-containing enzyme (selenoprotein) glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which detoxifies lipid peroxides using glutathione. However, through chemical controls using the (R) stereoisomer of RSL3 [(1R,3R)-RSL3] that does not bind GPX4, combined with inducible genetic knockdowns of GPX4 in colorectal cancer cell lines, we revealed in this study that GPX4 dependency does not always align with (S)-RSL3 sensitivity, thereby questioning the current characterization of GPX4 as the primary target of (S)-RSL3. Affinity pull-down mass spectrometry with modified (S)-RSL3 probes identified multiple selenoprotein targets, indicating broad selenoprotein inhibition. Further investigation of the therapeutic potential of broadly disrupting the selenoproteome as a therapeutic strategy in colorectal cancer showed that the selenoprotein inhibitor auranofin, an FDA-approved gold salt, chemically induced oxidative cell death and ferroptosis in colorectal cancer models in vitro and in vivo. Similarly, genetic perturbation of ALKBH8, a tRNA-selenocysteine methyltransferase required for selenoprotein translation, suppressed colorectal cancer growth. In summary, these findings recharacterize the mechanism of (S)-RSL3 beyond GPX4 inhibition and establish selenoproteome disruption as a colorectal cancer therapeutic strategy.
Significance: Chemoproteomic profiling reveals that RSL3 functions through pan-selenoprotein inhibition beyond GPX4 and identifies ALKBH8, a tRNA-selenocysteine methyltransferase essential for selenoprotein translation, as a therapeutic target to disrupt redox balance in colorectal cancer.
A related commentary was published in the August 1 issue.
Journal: Cancer Research (August 15 issue)
The gut microbiome has emerged as a key regulator of response to cancer immunotherapy. However, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms by which the microbiome influences immunotherapy is needed to identify strategies to optimize outcomes. To this end, we developed a mathematical model to obtain insights into the effect of the microbiome on the immune system and immunotherapy response. This model was based on (i) gut microbiome data derived from preclinical studies, (ii) mathematical modeling of the antitumor immune response, (iii) association analysis of microbiome profiles with model-predicted immune profiles, and (iv) statistical models that correlate model parameters with the microbiome. The model was used to investigate the complexity of murine and human studies on microbiome modulation. Comparison of model predictions with experimental observations of tumor response in the training and test datasets supported the hypothesis that two model parameters, the activation and killing rate constants of immune cells, are the most influential in tumor progression and are potentially affected by microbiome composition. Evaluation of the associations between the gut microbiome and immune profile indicated that the components and structure of the gut microbiome affect the activation and killing rate of adaptive and innate immune cells. Overall, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of microbiome–cancer interactions and offers a framework for understanding how microbiome interactions influence cancer treatment outcomes.
Significance: Integration of mathematical modeling and microbiome data reveals how gut microbiome components impact immune response, providing insights to optimize immunotherapy strategies.
This article is part of a special series on Driving Cancer Discoveries with Computational Research, Data Science, and Machine Learning/AI. Learn more about the role of the gut microbiome on immunotherapy responses in a recent post on the AACR blog.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (August 1 issue)
Purpose: Patients with residual nasopharyngeal carcinoma after receiving standard-of-care treatment have poor prognoses. In this trial, we aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of capecitabine maintenance therapy in patients with residual nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Patients and Methods: This open-label, single-arm, phase II trial was conducted at Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. We recruited patients of 18 to 70 years of age with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score of 0 to 1, histopathologically or cytologically confirmed nasopharyngeal carcinoma (without distant metastasis), who had residual disease after receiving definitive treatment. Patients received 1 year of capecitabine maintenance therapy. The primary endpoint was 2-year progression-free survival.
Results: Between January 1, 2019, and December 30, 2022, 111 patients were recruited and commenced capecitabine maintenance therapy for 1 year. After a median follow-up duration of 34.8 months (IQR = 30.5–45.2), progression-free survival was 92% at 1 year, 86% at 2 years, and 81% at 3 years. Adverse events were reported in 97.3% of patients. Hand-foot syndrome was the most common adverse event (59.5%). In addition, 28.7% of patients experienced grade 3 treatment-related adverse events, the most common of which was hand-foot syndrome (7.2%); no grade 4 or 5 adverse events were recorded. A total of 72.1% of patients received the full dosage of capecitabine, and 76.6% of patients completed the 1-year capecitabine maintenance therapy.
Conclusions: The antitumor efficacy of capecitabine maintenance therapy is promising, and the safety profile is manageable in patients with residual nasopharyngeal carcinoma after receiving standard-of-care treatment.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (August 15 issue)
Purpose: CB307 is a trispecific variable heavy-chain antibody fragment against prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), CD137, and human serum albumin. It is designed to mitigate hepatotoxicity by activating T cells only in PSMA-positive tumors and to increase drug half-life through albumin binding. This phase I study investigated the safety and tolerability of CB307 as monotherapy or in combination with pembrolizumab.
Patients and Methods: Patients who were heavily pretreated with PSMA-positive solid tumors were enrolled in the dose-escalation phase of CB307 monotherapy. The additional safety and efficacy of CB307 were assessed in the CB307 monotherapy expansion cohort and in combination with pembrolizumab.
Results: CB307 was administered to 75 patients. CB307 was given once every 7 days as monotherapy (N = 50) or in combination with pembrolizumab (N = 25). Two dose-limiting toxicities (grade 3 transient transaminitis) were observed. A total of three grade 3 transaminitis events (one in the monotherapy cohort and two in the combination cohort) were observed, and none involved bilirubin elevation. Durable RECIST responses were observed in two patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer enrolled in the 800 mg CB307 monotherapy and in one patient in the combination cohort (overall response rates: 11.1% and 7.1%, respectively). A disease control rate (DCR) of 50% was observed in patients enrolled in the 800 mg CB307 monotherapy cohort and 42.9% in the combination cohort. In a post hoc analysis, the response was numerically better in patients who had not received chemotherapy in the 6 months prior to starting CB307 (ORR = 20%, DCR = 60% vs. ORR = 0%, DCR = 37.5%). CB307 induces cytotoxic cell expansion in tumors and PD-L1 expression.
Conclusions: CB307 was well tolerated as a monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab, and tumor responses were observed in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
A related commentary was published in the August 15 issue.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Research
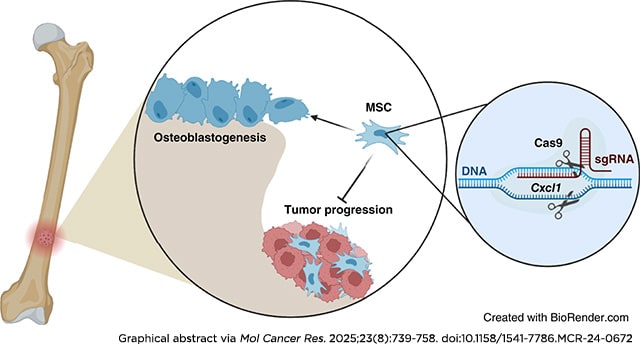
Bone metastasis continues to be the greatest challenge in treating patients with prostate cancer despite ongoing research. In bone, prostate cancer tumors hijack normal bone remodeling processes to drive cancer progression. However, it is unclear how these interactions drive bone-metastatic prostate cancer growth in the bone environment. To understand the mechanisms associated with bone-metastatic prostate cancer regulation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), we previously identified that bone-metastatic prostate cancer induces MSC expression of the pro-inflammatory chemokine CXCL8 and its mouse functional homologue Cxcl1. To date, there has been little to no information about the role of CXCL1/8 in MSC biology and its impact in the tumor–bone environment. Using genetic deletion of Cxcl1, we discovered a novel role for Cxcl1/8 in regulating MSC osteoblast differentiation, such that targeted deletion of Cxcl1 enhanced MSC osteoblastogenesis. Despite the osteogenic nature of prostate cancer, co-injection of Cxcl1 knockout (KO) MSCs with bone-metastatic prostate cancer in bone significantly suppressed tumor growth compared with co-injection with scrambled control (non-targeting) MSCs, even in the presence of three times more prostate cancer to MSCs. Furthermore, bulk RNA sequencing revealed immune response pathways, both in Cxcl1-KO MSCs and bone-metastatic prostate cancer tumors containing Cxcl1-KO MSCs. In support of this, Cxcl1-KO MSCs reduced immature neutrophils in the bone environment, while increasing monocytes. These findings demonstrate the importance of MSC-derived Cxcl1 in the bone microenvironment and highlight the importance of Cxcl1 in bone-metastatic prostate cancer progression.
Implications: MSC-derived Cxcl1 regulates prostate cancer progression in bone.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Therapeutics
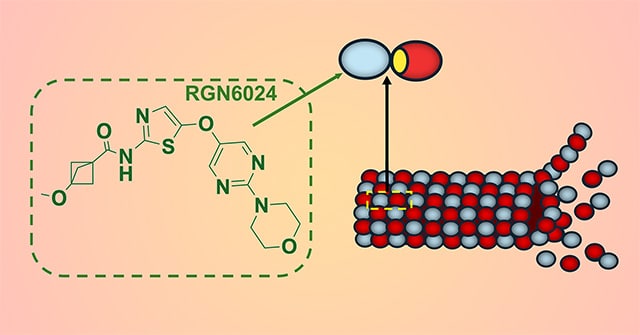
RGN6024 Is a Brain-Penetrant, Small-Molecule Tubulin Destabilizer for the Treatment of Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor in adults, with a median survival of ∼15 months. Given the poor survival with the currently approved treatments, new therapies are urgently needed. Microtubule-targeting agents (MTA) represent one of the most successful first-line therapies for cancers; however, the inability of approved MTAs to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) limits their use for central nervous system cancers. The development of novel MTAs with good BBB penetrance, decreased toxicity, and an ability to overcome drug-induced resistance is an attractive prospect. In this study, we describe the characterization of RGN6024, a brain-penetrant small-molecule tubulin destabilizer that binds the colchicine-binding site of tubulin. RGN6024 has excellent in vitro potency against GBM cell lines in viability assays with IC50 values in the low to mid nanomolar range. RGN6024 is less susceptible to common drug resistance mechanisms; its activity is unaffected by βIII-tubulin overexpression and it demonstrates good blood–brain penetration in in vivo mouse and rat models. With oral dosing, RGN6024 shows excellent BBB penetration in both mice (Cmax = 3,530 ng/g) and rats (Cmax = 1,667 ng/g). Drug efficacy was confirmed in two xenograft models. In a temozolomide-resistant LN-18 GBM xenograft model, RGN6024 showed a reduction in tumor growth when dosed orally at 7.5 or 15 mg/kg. Additionally, RGN6024 suppressed the growth of BT142 GBM cells in an orthotopic murine model and significantly prolonged survival. Taken together, these data provide support for the development of RGN6024 for the treatment of GBM.
This article was featured on the cover of the August issue.
Journal: Cancer Research Communications
Corticosteroids are frequently prescribed to patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) for palliation of cancer-related symptoms; however, the potential impact of baseline steroid use on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we evaluated clinical outcomes of 277 patients with NSCLC treated with ICI therapy at two academic institutions. Twenty-one patients (8%) were taking steroids at the start of ICIs. Patients on baseline steroids had a lower overall response rate with markedly shorter progression-free survival and overall survival compared with those not receiving steroids. In multivariate analysis, steroid use was the only significant independent risk factor for disease progression and mortality in both independent cohorts, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center (n = 88) and University of Southern California (n = 189). A baseline peripheral blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio <5 was a strong prognostic indicator; however, the prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio was absent in patients receiving steroids. Additionally, the baseline frequency of circulating CX3CR1+CD8+ T cells was substantially lower in patients on steroids. Using a bedside-to-bench approach, we found that concurrent steroid use significantly decreased antitumor efficacy of anti–PD-1 therapy and attenuated the increase of CX3CR1+CD8+ T cells in mice bearing MC38 tumors whereas discontinuation of steroid at the start of treatment did not make a negative impact on survival. Collectively, baseline steroid use was associated with worse outcomes and decreased frequency of circulating differentiated effector T cells in patients with NSCLC. Caution should be taken when interpreting the results from circulating immune-related biomarkers in patients on steroids.
Significance: The impact of corticosteroids, widely prescribed for palliation of cancer-related symptoms, on ICI therapy remains unclear. This study shows that baseline steroid use is a negative independent prognostic factor in patients with NSCLC undergoing ICI therapy and provides insights into the decreased T-cell effector differentiation and utility of predictive blood-based markers by steroids.