Editors’ Picks: Highlights from the AACR Journals
As you say farewell to summer, say hello to the latest installment of Editors’ Picks selected by the editors of the 10 AACR journals.
This month’s selections include a drug that can help overcome resistance to several targeted therapies, an investigation of how tumor-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit CAR T-cell efficacy, a new type of bispecific T-cell engager, and more. The abstracts of these studies are included below, and the full text of each article will be freely available for a limited time.
Journal: Blood Cancer Discovery
A Phase Ib/II Study of Ivosidenib with Venetoclax ± Azacitidine in IDH1-Mutated Myeloid Malignancies
The safety and efficacy of combining the isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) inhibitor ivosidenib (IVO) with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax (VEN; IVO + VEN) ± azacitidine (AZA; IVO + VEN + AZA) were evaluated in four cohorts of patients with IDH1-mutated myeloid malignancies (n = 31). Most (91%) adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The maximal tolerated dose was not reached. Composite complete remission with IVO + VEN + AZA versus IVO + VEN was 90% versus 83%. Among measurable residual disease (MRD)–evaluable patients (N = 16), 63% attained MRD-negative remissions; IDH1 mutation clearance occurred in 64% of patients receiving ≥5 treatment cycles (N = 14). Median event-free survival and overall survival were 36 [94% CI, 23-not reached (NR)] and 42 (95% CI, 42-NR) months. Patients with signaling gene mutations appeared to particularly benefit from the triplet regimen. Longitudinal single-cell proteogenomic analyses linked co-occurring mutations, antiapoptotic protein expression, and cell maturation to therapeutic sensitivity of IDH1-mutated clones. No IDH isoform switching or second-site IDH1 mutations were observed, indicating combination therapy may overcome established resistance pathways to single-agent IVO.
Significance: IVO + VEN + AZA is safe and active in patients with IDH1-mutated myeloid malignancies. Combination therapy appears to overcome resistance mechanisms observed with single-agent IDH-inhibitor use, with high MRD-negative remission rates. Single-cell DNA ± protein and time-of-flight mass-cytometry analysis revealed complex resistance mechanisms at relapse, highlighting key pathways for future therapeutic intervention.
This study was highlighted in the August issue.
Journal: Cancer Discovery

Rationally targeted therapies have transformed cancer treatment, but many patients develop resistance through bypass signaling pathway activation. PF-07284892 (ARRY-558) is an allosteric SHP2 inhibitor designed to overcome bypass-signaling-mediated resistance when combined with inhibitors of various oncogenic drivers. Activity in this setting was confirmed in diverse tumor models. Patients with ALK fusion-positive lung cancer, BRAFV600E-mutant colorectal cancer, KRASG12D-mutant ovarian cancer, and ROS1 fusion-positive pancreatic cancer who previously developed targeted therapy resistance were treated with PF-07284892 on the first dose level of a first-in-human clinical trial. After progression on PF-07284892 monotherapy, a novel study design allowed the addition of oncogene-directed targeted therapy that had previously failed. Combination therapy led to rapid tumor and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) responses and extended the duration of overall clinical benefit.
Significance: PF-07284892–targeted therapy combinations overcame bypass-signaling-mediated resistance in a clinical setting in which neither component was active on its own. This provides proof of concept of the utility of SHP2 inhibitors in overcoming resistance to diverse targeted therapies and provides a paradigm for accelerated testing of novel drug combinations early in clinical development.
This study was highlighted and featured on the cover of the August issue. A related commentary is available here.
Journal: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention
Background: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) accounts for 80% of all leukemias diagnosed in children. Although ALL age patterns are consistent across racial/ethnic groups, their incidence and mortality rates are highly variable. We assessed the age-standardized ALL incidence and mortality rates of Puerto Rican Hispanic (PRH) children and compared them with those of US mainland Hispanics (USH), non-Hispanic Whites (NHW), non-Hispanic Blacks (NHB), and Non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islanders (NHAPI).
Methods: Differences between racial/ethnic groups were assessed by estimating the standardized rate ratio (SRR) for 2010 to 2014. Secondary data analyses of the Puerto Rico Central Cancer Registry and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) databases were performed for the 2001 to 2016 period.
Results: PRH children had 31% lower incidence rates than USH, but 86% higher incidence rates than NHB. In addition, the incidence trends of ALL increased significantly from 2001 to 2016 among PRH and USH, with 5% and 0.9% per year, respectively. Moreover, PRH have a lower 5-year overall survival (81.7%) when compared with other racial/ethnic groups.
Conclusions: PRH children were found to have disparities in ALL incidence and mortality rates compared with other racial/ethnic groups in the US. Additional research is warranted to identify the genetic and environmental risk factors that may be associated with the disparities observed.
Impact: This is the first study reporting the incidence and mortality rates of childhood ALL for PRH and making comparisons with other racial/ethnic groups in the US.
This study was highlighted and featured on the cover of the August issue. A related commentary is available here.
Journal: Cancer Immunology Research
Intratumoral T-cell dysfunction is a hallmark of pancreatic tumors, and efforts to improve dendritic cell (DC)-mediated T-cell activation may be critical in treating these immune therapy unresponsive tumors. Recent evidence indicates that mechanisms that induce dysfunction of type 1 conventional DCs (cDC1) in pancreatic adenocarcinomas (PDAC) are drivers of the lack of responsiveness to checkpoint immunotherapy. However, the impact of PDAC on systemic type 2 cDC2 development and function has not been well studied. Herein, we report the analysis of 3 cohorts, totaling 106 samples, of human blood and bone marrow (BM) from patients with PDAC for changes in cDCs. We found that circulating cDC2s and their progenitors were significantly decreased in the blood of patients with PDAC, and repressed numbers of cDC2s were associated with poor prognosis. Serum cytokine analyses identified IL6 as significantly elevated in patients with PDAC and negatively correlated with cDC numbers. In vitro, IL6 impaired the differentiation of cDC1s and cDC2s from BM progenitors. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of human cDC progenitors in the BM and blood of patients with PDAC showed an upregulation of the IL6/STAT3 pathway and a corresponding impairment of antigen processing and presentation. These results suggested that cDC2s were systemically suppressed by inflammatory cytokines, which was linked to impaired antitumor immunity.
This study was featured on the cover of the August issue.
Journal: Cancer Prevention Research
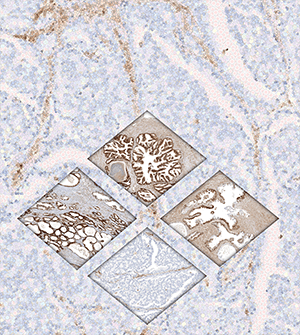
Glutathione S-transferase pi 1 (GSTP1) is lowly expressed in normal prostate luminal cells and becomes induced in most proliferative inflammatory atrophy (PIA) lesions. GSTP1 becomes silenced in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) and prostate adenocarcinoma (CaP) via cytosine-phospho-guanine (CpG) island promoter hypermethylation. However, GSTP1 methylation patterns in PIA and PIN, and their relationship to patterns in CaP are poorly understood. We used bisulfite genomic sequencing to examine patterns of GSTP1 promoter CpG island methylation in laser capture microdissected benign, PIA, PIN, and CaP regions from 32 subjects that underwent radical prostatectomy. We analyzed 908 sequence clones across 24 normal epithelium, 37 PIA, 18 PIN, and 23 CaP regions, allowing assessment of 34,863 CpG sites with allelic phasing. Normal and PIA lesions were mostly unmethylated with 0.52 and 1.3% of total CpG sites methylated, respectively. PIN and CaP lesions had greater methylation with 24% and 51% of total CpG sites methylated, respectively. The degree of GSTP1 methylation showed progression from PIA << PIN < CaP. PIN lesions showed more partial methylation compared with CaP lesions. Partially methylated lesions were enriched for methylation changes at AP1 and SP1 transcription factor binding sites. These results demonstrate that methylation density in the GSTP1 CpG island in PIN was intermediate relative to that in normal prostate epithelium/PIA and CaP lesions. These results are consistent with gradual spreading of DNA methylation centered at the SP1/AP1 transcription factor binding sites in precursor lesions, with subsequent spreading of methylation across the entire CpG island in transition to CaP.
Prevention Relevance: DNA hypermethylation at the GSTP1 promoter progressively spreads from being unmethylated in normal prostate to intermediate levels in precursor lesions to extensive methylation in cancer. This molecular progression of GSTP1 promoter methylation patterns in early prostate carcinogenesis could be useful for identification and interception of prostate cancer precursors.
This study was featured on the cover of the August issue.
Journal: Cancer Research (August 1 issue)
Cancer metastasis is an extremely complex process affected by many factors. An acidic microenvironment can drive cancer cell migration toward blood vessels while also hampering immune cell activity. Here, we identified a mechanism mediated by sialyltransferases that induces an acidic tumor-permissive microenvironment (ATPME) in BRCA1-mutant and most BRCA1-low breast cancers. Hypersialylation mediated by ST8SIA4 perturbed the mammary epithelial bilayer structure and generated an ATPME and immunosuppressive microenvironment with increased PD-L1 and PD1 expressions. Mechanistically, BRCA1 deficiency increased expression of VEGFA and IL6 to activate TGFβ–ST8SIA4 signaling. High levels of ST8SIA4 led to accumulation of polysialic acid (PSA) on mammary epithelial membranes that facilitated escape of cancer cells from immunosurveillance, promoting metastasis and resistance to αPD1 treatment. The sialyltransferase inhibitor 3Fax-Peracetyl Neu5Ac neutralized the ATPME, sensitized cancers to immune checkpoint blockade by activating CD8 T cells, and inhibited tumor growth and metastasis. Together, these findings identify a potential therapeutic option for cancers with a high level of PSA.
Significance: BRCA1 deficiency generates an acidic microenvironment to promote cancer metastasis and immunotherapy resistance that can be reversed using a sialyltransferase inhibitor.
Journal: Cancer Research (August 15 issue)
Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit the Efficacy of CAR T Cells against Solid Tumors
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has shown remarkable success in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Unfortunately, it has limited efficacy against solid tumors, even when the targeted antigens are well expressed. A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of CAR T-cell therapy resistance in solid tumors is necessary to develop strategies to improve efficacy. Here we report that solid tumors release small extracellular vesicles (sEV) that carry both targeted tumor antigens and the immune checkpoint protein PD-L1. These sEVs acted as cell-free functional units to preferentially interact with cognate CAR T cells and efficiently inhibited their proliferation, migration, and function. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking tumor sEV secretion not only boosted the infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR T cells but also improved endogenous antitumor immunity. These results suggest that solid tumors use sEVs as an active defense mechanism to resist CAR T cells and implicate tumor sEVs as a potential therapeutic target to optimize CAR T-cell therapy against solid tumors.
Significance: Small extracellular vesicles secreted by solid tumors inhibit CAR T cells, which provide a molecular explanation for CAR T-cell resistance and suggests that strategies targeting exosome secretion may enhance CAR T-cell efficacy.
A commentary on this study is available here.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (August 1 issue)
Purpose: The majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) are driven by constitutively activated KIT/PDGFRA kinases and are susceptible to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. During treatment, most of these tumors will develop secondary mutations in KIT or PDGFRA inducing drug resistance, so there is an unmet need for novel therapies. We tested the efficacy of IDRX-42, a novel selective KIT inhibitor with high activity toward the most relevant KIT mutations, in 4 GIST xenograft models.
Experimental Design: NMRI nu/nu mice were transplanted with patient-derived GIST xenograft models UZLX-GIST9 (KIT:p.P577del;W557LfsX5;D820G), UZLX-GIST2B (KIT:p.A502_Y503dup), UZLX-GIST25 (KIT:p.K642E), and the cell line-derived model GIST882 (KIT:p.K642E). Mice were treated daily with vehicle (control), imatinib (100 mg/kg), sunitinib (20 mg/kg), avapritinib (5 mg/kg), or IDRX-42 (10 mg/kg, 25 mg/kg). Efficacy was assessed by tumor volume evolution, histopathology, grading of histologic response, and IHC. The Kruskal–Wallis and Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests were used for statistical analysis, with P < 0.05 considered as significant.
Results: IDRX-42 (25 mg/kg) caused tumor volume shrinkage in UZLX-GIST25, GIST882, and UZLX-GIST2B, with a relative decrease to 45.6%, 57.3%, and 35.1% on the last day as compared with baseline, and tumor growth delay (160.9%) compared with control in UZLX-GIST9. Compared with controls, IDRX-42 (25 mg/kg) induced a significant decrease in mitosis. In UZLX-GIST25 and GIST882 grade 2–4 histologic response with myxoid degeneration was observed in all IDRX-42 (25 mg/kg)-treated tumors.
Conclusions: IDRX-42 showed significant antitumor activity in patient- and cell line–derived GIST xenograft models. The novel kinase inhibitor induced volumetric responses, decreased mitotic activity, and had antiproliferative effects. In models with KIT exon 13 mutation IDRX-42 induced characteristic myxoid degeneration.
This article was highlighted in the August 1 issue.
Journal: Clinical Cancer Research (August 15 issue)
Purpose: Acquired RET fusions have been reported at resistance to treatment with EGFR inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, a multicenter cohort of patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers treated with osimertinib and selpercatinib for RET fusion-mediated osimertinib resistance has not previously been published.
Patients and Methods: Patients who received selpercatinib in combination with osimertinib on a prospective expanded access clinical trial (NCT03906331) and single-patient compassionate use programs across five countries were centrally analyzed. All patients had advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC with a RET fusion detected from tissue or plasma following osimertinib therapy. Clinicopathologic and outcomes data were collected.
Results: Fourteen patients with EGFR-mutant and RET fusion-positive lung cancers who experienced prior progression on osimertinib received osimertinib and selpercatinib. EGFR exon 19 deletions (±T790M, 86%) and non-KIF5B fusions (CCDC6-RET 50%, NCOA4-RET 36%) predominated. Osimertinib 80 mg daily and selpercatinib 80 mg twice daily were the most commonly administered dosages. The response rate, disease control rate, and median treatment duration were 50% [95% confidence interval (CI), 25%-75%, n = 12], 83% (95% CI, 55%-95%), and 7.9 months (range, 0.8-25+), respectively. Resistance was complex, involving EGFR on-target (EGFR C797S), RET on-target (RET G810S), and off-target (EML4-ALK/STRN-ALK, KRAS G12S, BRAF V600E) mechanisms; RET fusion loss; or polyclonal mechanisms.
Conclusions: For patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC with an acquired RET fusion as a mechanism of EGFR inhibitor resistance, the addition of selpercatinib to osimertinib was feasible and safe and offered clinical benefit, supporting the prospective evaluation of this combination.
This article was highlighted in the August 15 issue, and a commentary is available here.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Research
New Western-style diet 1 (NWD1), a purified diet establishing mouse exposure to key nutrients recapitulating levels that increase human risk for intestinal cancer, reproducibly causes mouse sporadic intestinal and colonic tumors reflecting human etiology, incidence, frequency, and lag with developmental age. Complex NWD1 stem cell and lineage reprogramming was deconvolved by bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing, single-cell Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing, functional genomics, and imaging. NWD1 extensively, rapidly, and reversibly, reprogrammed Lgr5hi stem cells, epigenetically downregulating Ppargc1a expression, altering mitochondrial structure and function. This suppressed Lgr5hi stem cell functions and developmental maturation of Lgr5hi cell progeny as cells progressed through progenitor cell compartments, recapitulated by Ppargc1a genetic inactivation in Lgr5hi cells in vivo. Mobilized Bmi1+, Ascl2hi cells adapted lineages to the nutritional environment and elevated antigen processing and presentation pathways, especially in mature enterocytes, causing chronic, protumorigenic low-level inflammation. There were multiple parallels between NWD1 remodeling of stem cells and lineages with pathogenic mechanisms in human inflammatory bowel disease, also protumorigenic. Moreover, the shift to alternate stem cells reflects that the balance between Lgr5-positive and -negative stem cells in supporting human colon tumors is determined by environmental influences. Stem cell and lineage plasticity in response to nutrients supports historic concepts of homeostasis as a continual adaptation to environment, with the human mucosa likely in constant flux in response to changing nutrient exposures.
Implications: Although oncogenic mutations provide a competitive advantage to intestinal epithelial cells in clonal expansion, the competition is on a playing field dynamically sculpted by the nutritional environment, influencing which cells dominate in mucosal maintenance and tumorigenesis.
This article was highlighted in the August issue.
Journal: Molecular Cancer Therapeutics
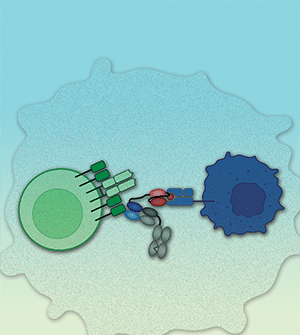
CD3 bispecific T-cell engagers (TCE), comprised of a tumor-targeting domain linked to a CD3 binding domain, function by bridging target-positive tumors and CD3-expressing effector T cells enabling redirected T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells. Although the majority of CD3 bispecific molecules in clinical development incorporate tumor-targeting antibody-based binding domains, many tumor-associated antigens derive from intracellular proteins and are not accessible to targeting via antibody. Intracellular proteins processed into short peptide fragments and presented on the cell surface by MHC proteins are recognized by T-cell receptors (TCR) on the surface of T cells. Here we describe the generation and preclinical evaluation of ABBV-184, a novel TCR/anti-CD3 bispecific composed of a highly selective soluble TCR that binds a peptide derived from the oncogene survivin (BIRC5) bound to the class I MHC allele human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A*02:01 expressed on tumor cells, linked to a specific binder to the CD3 receptor on T cells. ABBV-184 drives an optimal distance between T cell and target cell thereby enabling sensitive recognition of low-density peptide/MHC targets. Consistent with the expression profile of survivin across a broad range of both hematologic and solid tumors, treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines with ABBV-184 results in T-cell activation, proliferation, and potent redirected cytotoxicity of HLA-A2-positive target cell lines, both in vitro and in vivo, including patient-derived AML samples. These results indicate that ABBV-184 is an attractive clinical candidate for the treatment of patients with AML and NSCLC.
This study was highlighted and featured on the cover of the August issue.
Journal: Cancer Research Communications
The tumor suppressor TP53 is the most frequently mutated gene in cancer and is mutationally inactivated in 50% of sporadic tumors. Inactivating mutations in TP53 also occur in Li Fraumeni syndrome (LFS). In addition to germline mutations in TP53 in LFS that completely inactivate this protein, there are many more germline mutant forms of TP53 in human populations that partially inactivate this protein: we call these partially inactivating mutations “hypomorphs.” One of these hypomorphs is a SNP that exists in 6%–10% of Africans and 1%–2% of African Americans, which changes proline at amino acid 47 to serine (Pro47Ser; P47S). We previously showed that the P47S variant of p53 is intrinsically impaired for tumor suppressor function, and that this SNP is associated with increased cancer risk in mice and humans. Here we show that this SNP also influences the tumor microenvironment, and the immune microenvironment profile in P47S mice is more protumorigenic. At basal levels, P47S mice show impaired memory T-cell formation and function, along with increased anti-inflammatory (so-called “M2”) macrophages. We show that in tumor-bearing P47S mice, there is an increase in immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells and decreased numbers of activated dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, along with evidence for increased T-cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Finally, we show that P47S mice demonstrate an incomplete response to anti-PD-L1 therapy. Our combined data suggest that the African-centric P47S variant leads to both intrinsic and extrinsic defects in tumor suppression.
Significance: Findings presented here show that the P47S variant of TP53 influences the immune microenvironment, and the immune response to cancer. This is the first time that a naturally occurring genetic variant of TP53 has been shown to negatively impact the immune microenvironment and the response to immunotherapy.