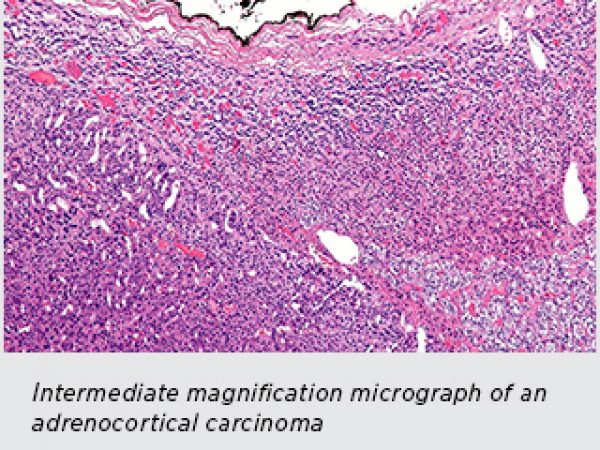
Adrenocortical Carcinoma

Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare disease in which cancer cells form in the outer layer of the adrenal gland. The adrenal gland has two parts. The outer layer is the adrenal cortex, where important hormones are produced that balance the water and salt in the body, help keep blood pressure normal, and help control the body’s use of protein, fat, and carbohydrates.
A tumor of the adrenal cortex may be functioning (makes more hormones than normal) or nonfunctioning (does not make hormones). Most adrenocortical tumors are functioning. The hormones made by functioning tumors may cause certain signs or symptoms of disease.
Adrenocortical carcinoma is also called cancer of the adrenal cortex. Having certain genetic conditions increases the risk of adrenocortical carcinoma. The center of the adrenal gland is the adrenal medulla. Cancer that forms in the adrenal medulla is called pheochromocytoma.
Adrenocortical Carcinoma Treatment (PDQ®)Source: National Cancer Institute